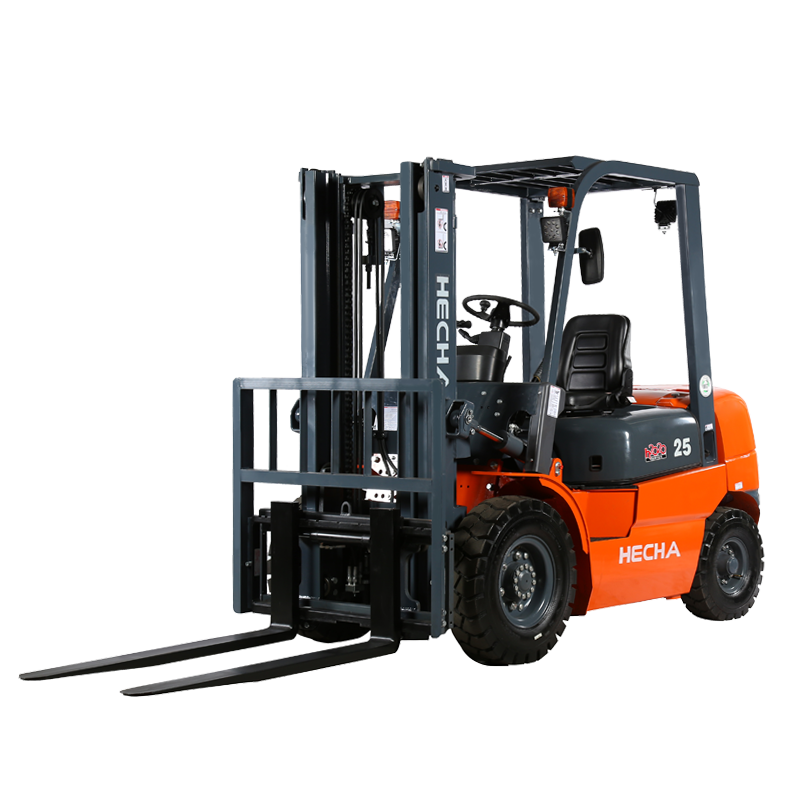
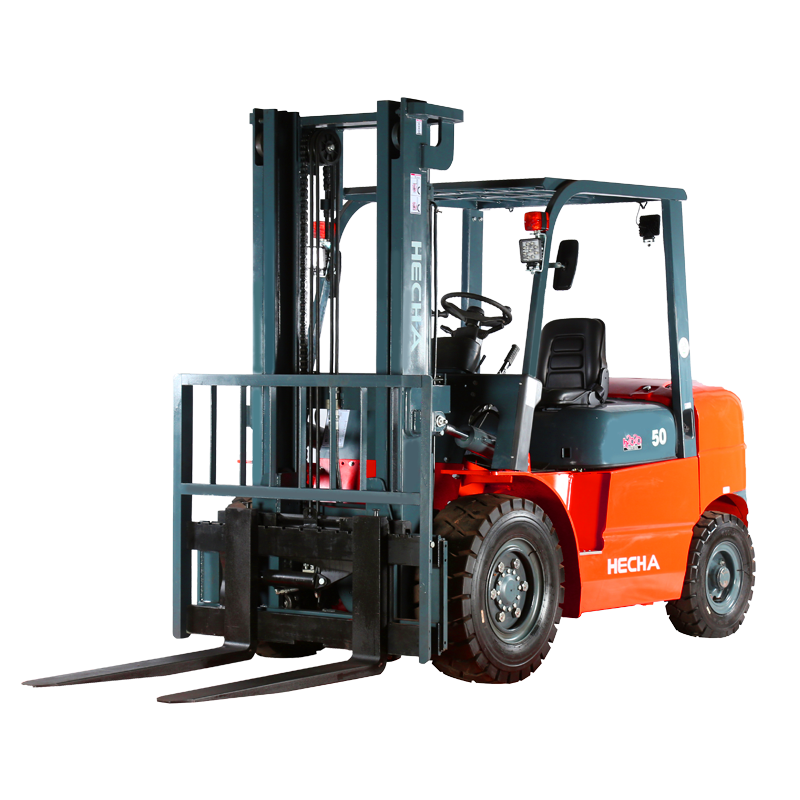
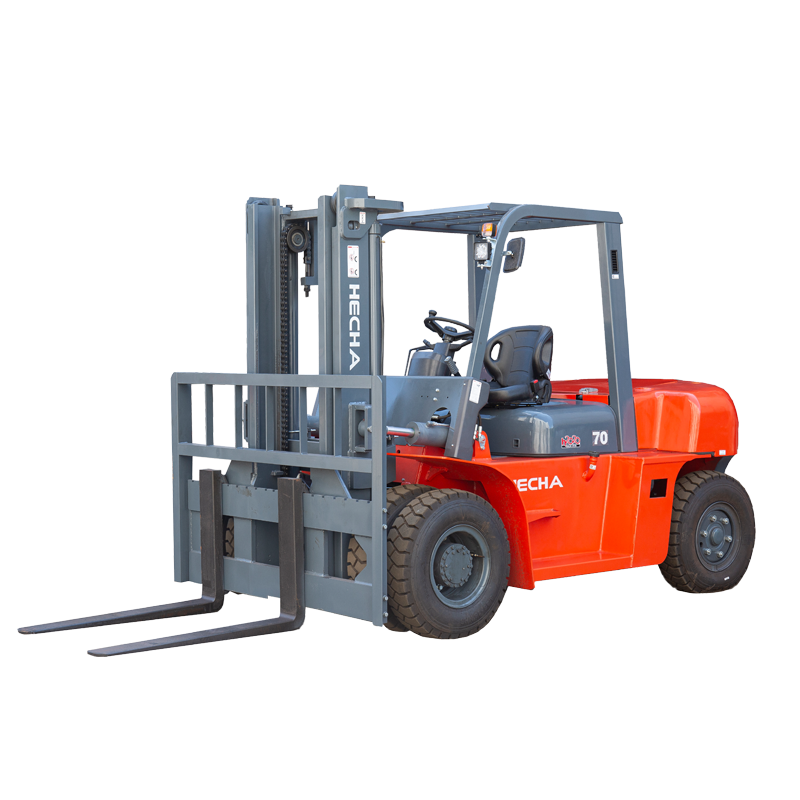
The counterbalance type electric stacker is a widely used material handling device, valued for its ability to lift, transport, and stack heavy loads efficiently. Like all industrial equipment, proper operation and maintenance are essential, but occasional issues may arise during its use.
Overview of counterbalance type electric stacker
A counterbalance type electric stacker is designed with a rear counterweight to balance the load lifted at the forks, eliminating the need for front stabilizers. This design allows operators to handle pallets in confined spaces while maintaining stability and efficiency. These stackers are powered by electric motors, usually with rechargeable batteries, and are equipped with hydraulic systems for lifting and lowering loads.
Key components include the lifting mast, forks, battery, hydraulic pump, control system, and wheels. Each part plays a critical role in ensuring smooth operation, and any malfunction in one component can affect overall performance.
Industry applications for counterbalance type electric stackers span warehousing, logistics, retail, and light manufacturing, where moving heavy pallets safely and efficiently is essential.
Common operational issues
Operators often encounter several recurring problems with counterbalance type electric stackers, which can be broadly categorized into electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, and operational issues.
Electrical problems
Electrical issues are among the most common causes of downtime for counterbalance type electric stackers. Typical electrical problems include:
- Battery failure or insufficient charge: Batteries may fail to hold a charge due to age, improper charging cycles, or environmental factors such as extreme temperatures. Operators may notice reduced runtime or failure to start.
- Faulty wiring or connections: Loose or corroded wires can interrupt power flow, causing intermittent operation or complete failure.
- Control system errors: Malfunctions in the control panel can result in inconsistent movement, delayed response to commands, or error codes.
Troubleshooting methods for electrical problems involve inspecting the battery for voltage levels, checking all wiring connections for corrosion or looseness, and testing the control panel for proper function. Ensuring that operators follow recommended charging procedures can prevent many common electrical failures.
Mechanical problems
Mechanical failures may stem from wear and tear, improper operation, or environmental factors. Common mechanical issues include:
- Worn wheels or casters: Over time, wheels can wear unevenly or become damaged, leading to unstable movement or difficulty maneuvering the stacker.
- Fork or mast deformation: Heavy or unbalanced loads can cause bending or misalignment of the forks or mast, impairing lifting capabilities.
- Steering difficulties: The steering mechanism may become stiff or unresponsive due to lubrication issues or worn components.
Troubleshooting methods for mechanical problems generally involve routine inspections, checking alignment, lubricating moving parts, and replacing worn components. Operators should also ensure loads are within the rated capacity of the stacker to prevent premature wear.
Hydraulic problems
The hydraulic system is crucial for lifting and lowering loads on a counterbalance type electric stacker. Common issues include:
- Slow lifting or lowering: This may indicate low hydraulic fluid levels, air in the hydraulic lines, or worn seals.
- Hydraulic leaks: Leaks in hoses, cylinders, or connections can reduce performance and create safety hazards.
- Inconsistent lifting: Malfunctioning pumps or valves can cause the lift to operate unevenly or fail under load.
Troubleshooting methods involve checking hydraulic fluid levels, inspecting hoses and cylinders for leaks, bleeding air from the system, and ensuring pumps and valves function correctly. Routine preventive maintenance of the hydraulic system can significantly reduce downtime.
Operational problems
Sometimes, operational issues arise not from equipment failure but from improper use. Common operator-related problems include:
- Overloading: Exceeding the rated capacity can lead to instability, equipment damage, or accidents.
- Improper maneuvering: Sudden turns, high speeds, or uneven surfaces can reduce stacker performance and increase wear.
- Neglecting safety protocols: Failure to follow safety procedures may result in equipment damage or personal injury.
Troubleshooting methods include retraining operators, enforcing safety guidelines, and implementing standard operating procedures for lifting, transporting, and stacking loads.
Step-by-step troubleshooting methods
Effectively troubleshooting a counterbalance type electric stacker requires a systematic approach. The following steps can help identify and resolve issues:
- Visual inspection: Check for visible signs of wear, leaks, or damage to the forks, wheels, hydraulic system, and battery.
- Operational test: Observe the stacker in action to identify unusual sounds, slow responses, or erratic behavior.
- Check power and battery: Ensure the battery is charged and connections are secure. Measure voltage levels if necessary.
- Inspect hydraulic system: Verify fluid levels, check for leaks, and test lift and lower functions for smoothness.
- Assess mechanical components: Check wheels, steering, forks, and mast alignment. Lubricate or replace worn parts.
- Review control systems: Inspect electrical wiring and control panels for loose connections or error codes.
- Test under controlled load: Apply a light load and gradually increase to the rated capacity to confirm proper performance.
Following these steps ensures a structured approach that reduces the likelihood of overlooking problems and ensures safety and efficiency.
Preventive maintenance tips
Many issues with counterbalance type electric stackers can be avoided through preventive maintenance. Key practices include:
- Regular battery checks: Maintain proper charging cycles and inspect batteries for damage.
- Routine lubrication: Lubricate moving parts such as wheels, steering joints, and hydraulic components.
- Scheduled inspections: Regularly check forks, mast, wheels, and hydraulic hoses for wear and damage.
- Operator training: Ensure operators understand load limits, safe maneuvering practices, and emergency procedures.
- Environment control: Store the stacker in conditions that avoid extreme temperatures or high humidity, which can affect electrical and hydraulic systems.
Preventive maintenance not only extends the lifespan of the stacker but also reduces the frequency of emergency troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting table for common issues
| Problem | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting Method |
|---|---|---|
| Stacker won’t start | Battery low or faulty wiring | Check battery charge, inspect wiring and connections |
| Forks move slowly | Low hydraulic fluid or air in system | Refill fluid, bleed air from hydraulic lines |
| Stacker unstable | Overloading or wheel wear | Reduce load, inspect wheels, ensure proper tire pressure |
| Erratic movement | Faulty control panel or loose connections | Inspect control panel, tighten wiring connections |
| Hydraulic leak | Damaged hoses or seals | Inspect and replace damaged hoses or seals |
This table provides a quick reference for operators and maintenance personnel to address common issues efficiently.
Conclusion
Understanding common troubleshooting methods for a counterbalance type electric stacker is essential for maximizing productivity, minimizing downtime, and ensuring safe operation. By addressing electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, and operational issues systematically, warehouse managers and operators can maintain optimal performance. Implementing preventive maintenance, operator training, and structured troubleshooting procedures ensures that counterbalance type electric stackers remain reliable assets in any material handling environment.
Regular attention to performance, safety, and maintenance not only extends the equipment’s lifespan but also improves overall warehouse efficiency and reduces operational risks.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español